Arthrosis or osteoarthrosis of the knee joint is a disease that occurs in the background of dystrophic changes with subsequent connective tissue growth.There are many factors that affect the development of the disease, but they all lead to a violation of metabolism in the cartilage.In medical literature, arthrosis of the knee joint is called gonarthrosis.
According to statistics, gonarthrosis occupies a major position in the frequency of incidents between other arthrosis.The disease leads to severe discomfort, which can be painful while walking and resting.
Knowledge of early symptoms will help suspect the pathological development and cure it in the early stages.
Cause
According to medical classification, there are major and secondary gonarthrosis or knee joint arthrosis.
Knee joint arthrosis can occur in the background of various diseases or acts as their complications.When, due to unclear history or clinical picture, the right cause cannot be established, gonarthrosis is called primary, but if the cause is known, then the arthrosis is called secondary.
Arthrosis develops with age in almost everyone, on average, this period begins after 45-50 years of life.
Courses and pathogenesis of primary and secondary arthrosis are the same and do not depend on the cause of the incident.
The most common causes of arthrosis and osteoarthrosis of the knee joint are:
- traumatic damage to the knee;
- deformed together inside and outside;
- shortening one lower limb;
- abnormal hypermobility joints;
- chondroblast displacement;
- Cartilage calcinosis;
- femur and tibia osteomyelitis;
- rheumatoid arthritis or any other etiology;
- glucose metabolism;
- Metabolic diseases and hormone diseases.
Injury.After receiving a knee injury in the joint cavity, inflammation with a large focus of the alliteration can develop.After the loss of pro -inflammation agents, the repair or arthrosis process is activated.
Often, the disease occurs in a broken background with ligaments and damage to the bag and the surface of the cartilage.

Congenital deformation.Valgus or variable deformation is found to be very frequent and without proper correction can be complicated by sclerotic changes in the knee.This is due to the fact that one of the knees falls more than the load than it should.
Shortening any bottom.As well as deformation, in the pathogenesis of disease development, improper weight distribution of the knee plays a role.
Knee hypermors.In this case, wearing a cartilage of the knee joint can occur with subsequent degeneration and degeneration into the arthrosis.Hypermorsion often leads to spontaneous dislocation and joint capsule sprains.
Displasia is watery.Due to improper development of the motor surface in the knee joint, the pathological growth of connective tissue occurs.
Calcinosis joint.These pathogenesis are based on the deposition of salt into the joint cavity and the formation of certain sediment, which causes calcification with subsequent osteoarthritis.
Osteomyelitis.Bacterial diseases of inflammation where the destruction of bone and joints occurs.First, ankylosis and only sclerosis are then formed.
Arthritis any etiology.The most dangerous is rheumatoid arthritis, accompanied by heart and joint autoimmune lesions.
Diabetes, such as metabolic disorders, lead to infarction of nutrients into the joints and cartilage.
Obesity.With large weight, a large load is on the knee while walking and in a standing position.As a result of constant pressure, blood flow to the knee joint decreases, and the atrophy with the dysfunction develops.
Symptom
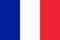
Symptoms with knee joint arthrosis depend on the level of pathological process.Based on this, analyzing their symptoms and growth rates, you can evaluate the scale of change in cartilage tissue.
Symptoms of knee arthrosis:
- the presence of pathological sounds during movement;
- pain after load or rest;
- reduction in function;
- edema and joint improvement;
- pathological dislocation, fractures and subluxation;
- Temporary jamming that can occur when flexion and extension of joints.
Clicks and crisis are not noticed immediately, and if they notice, they do not pay close attention.Pathological sounds discover the idea that the pathological process with salt deposition or the formation of osteophytes occurs in the cartilage gap.
Pain occurs due to the formation of calcinates or osteophytes.Initially, the pain syndrome was not stated, then only appeared in the morning and passed after lunch, with the progression of the disease, pain could occur at rest.
The decline in joint function is shown in the stiffness of movement and the decrease in their amplitude.Depending on the stage, the movement constraints can last some time and pass the rest.
Edema is caused by inflammation and synovial liquid hypersecretion.There is also an option when the skin is inflamed over the joints.Such symptoms can be with red or rheuminative fever.
Dislocation and subluxation occur due to the process for the bone and knee ligaments.
Clushing is a situation where movements where the axis is limited.Such symptoms indicate the neglect of the process and the need for complex treatment.
The degree of arthrosis
Classification of osteoarthritis according to the following signs:
- radiological symptoms;
- clinical manifestations;
- Laboratory data.
The most common and simple classification is radiology, it is simple and easy to understand even for people without medical education.
Based on X -Rays, four degrees of arthrosis in the knee joint are distinguished:
- The reduction of joint gaps is small, and there is no osteophytes;
- The intererspoint gap is not bound, but there are small signs of calcinates or osteophytes;
- The intererspoint gap has a narrow expression, there is osteophytes, joint deformation begins;
- Lack of joint gap, bone deformation, ankylose and distrophy.
About the clinical picture, the following stages are distinguished:
- Symptoms of mild degree are not important, occur in the morning and pass 30-60 minutes after waking up;
- The average degree is a clear symptom, a feeling of discomfort passes before lunch, swelling is not important, it develops quickly without treatment;
- Severe degrees - characterized by persistent pain, discomfort at rest, morning stiffness has not passed until dinner, ankylose, burgis and knee joint sinusitis develop.
Laboratory tests are taken into account, soy indications and leukocytes are evaluated.It is also necessary to check the presence of rheumatoid factors.
Diagnostic method
The diagnosis of knee joint arthrosis is not complicated, but requires certain skills from the doctor.
Two types of diagnostic steps are distinguished:
- Laboratory diagnostics;
- Instrumental diagnostics.
For the right diagnosis, each method needs to be taken into account and analyzing the picture as a whole.
Laboratory
If arthrosis is suspected, the attending physician prescribes the following test:
- general blood and urine tests;
- biochemical blood tests;
- Determination of antibodies to rheumatoid factors;
- Determination of antibodies to their own cells.
Laboratory data does not carry out information on the level of development of the disease.
Instrumental
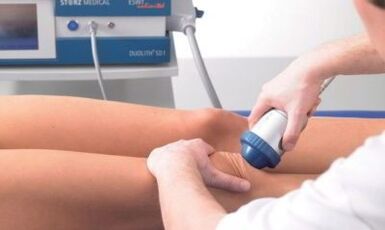
Diagnosis of instrumental arthrosis includes the following methods:
- Radiography in two standard projections;
- minimal invasive arthroscopy;
- UZD exams;
- Ct;
- MRI;
- Scintigraphy (according to the clues).
Radiation diagnostics are intended to determine changes in the joints and to assess the condition of the cartilage.
Treatment
Treatment of knee joint arthrosis is a long process.The duration of treatment is due to the fact that the repair of cartilage tissue occurs very slowly, and in some cases, it is impossible to restore the joints.
Modern methods of treating arthrosis in the knee joint include comprehensive steps aimed at eliminating inflammation, normalizing lifestyle, and improving cartilage tissue metabolism.
There are such methods of therapy:
- drug therapy;
- Exercise and massage therapy;
- People's Medicine;
- Surgical intervention.
Doctors prescribe treatment based on the duration of the disease, stage of development and clinical manifestations.
Medication
Drug therapy is intended to relieve pain and inflammation.For this purpose, the following drugs are prescribed:
- non -steroid anti -intiflammatory;
- Chondroprotectors;
- glucocorticoid;
- Cytostatic.
Tablets from knee joint arthrosis have many side effects, in the treatment needed to monitor the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys.
Often, medicines for arthrosis are prescribed for long periods of time, so the least toxic drugs should be selected.
Training
Arthrosis treatment using exercise therapy is intended to strengthen the muscles and knee ligaments.With the doses in the cartilage of the diseased joints, the metabolism increases, and the regenerative process is accelerated.
Exercises should be selected individually taking into account the level of patient disease and physical ability.
Massage
Knee joint massage allows you to increase blood flow and relieve discomfort.Proper massage can prevent the appearance of ankyloses and fake joints.
Folk
Treatment of knee joint arthrosis at home cannot be the main method for combating pathology, or can only act in addition to the drug.

Home treatment includes:
- weight loss;
- normalization of labor hygiene and compliance with the regime of the day;
- The struggle against inflammation.
Anti -anti -anti -herbs are owned by such herbs:
- Tincture from Thyme and St John's Wort;
- Burdock leaf;
- white cabbage leaves;
- Infusions and decoctions from dandelion and chamomile.
Operation
This operation is prescribed ineffective conservative therapy or at the request of the patient.One of the main indicators for surgical intervention is the 4th stage of disease by radiological features.
During surgery, the surgeon can replace the joints with endoprosthesis or change one of its parts.